- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
03-25-2020 08:36 AM in
Tech TalkThe Wi-Fi calling has the following Benefits for the customers –
- Use your prevailing phone number. No need for separate Airtel/Jio pack, 3rd party app or logins.
- Calls without any mobile signal.
- If you’re in a strong Wi-Fi radius, you would get better indoor coverage and faster connectivity
- This results in clear conversations
To start —
- Open the Settings app on your smartphones
- The processes on Android can differ from phone to phone. However, on most smartphones, it will be under SIM cards and Mobile Networks setting inside the SIM settings page.
What are the extra charges?
Airtel and Jio will not charge any extra cost for VoWi-Fi calling. However, some data will be consumed from the Wi-Fi network you are using.
Voice over Wi-Fi (VoWiFi) is a term typically employed to describe the delivery of commercial telephony services using Voice over IP (VoIP) technologies from mobile devices connected across Wi-Fi. This is typically counter to alternatives, predominantly Voice over LTE (VoLTE), in which a mobile network operator’s (MNO’s) licensed spectrum (i.e. 4G LTE) is used to carry packetized voice. Broadly speaking, VoWiFi terminology is assigned to all core IMS services accessed from unlicensed spectrum and across untrusted access infrastructures, such as public Wi-Fi access points. VoWiFi is used synonymously to describe the GSMAs permanent reference document IR.51: IMS Profile for Voice, Video and SMS over untrusted Wi-Fi access.
While over-the-top (OTT) mobile communications services may also employ Wi-Fi, where possible, to prevent using a subscriber’s (licensed) data plan, this is not typically referred to as VoWiFi as these services are not tightly integrated with a MNOs global service offering and infrastructure.
Employing VoWiFi enables MNOs (or MVNOs) to quickly and easily extend their coverage or service range without costly radio access network (RAN) infrastructure build-outs, investing in new licensed spectrum or engaging in complex roaming agreements. Following the 3GPP reference architecture defined within the 3GPP’s TS 23.402 (Architecture enhancements for non-3GPP [IP] accesses), connectivity from the mobile handset to the evolved packet core (EPC) is over the S2b reference interface via an enhanced packet data gateway (ePDG) function. The specification covers policy control, charging, authentication and handover between untrusted and trusted access infrastructures for both roaming and non-roaming scenarios.
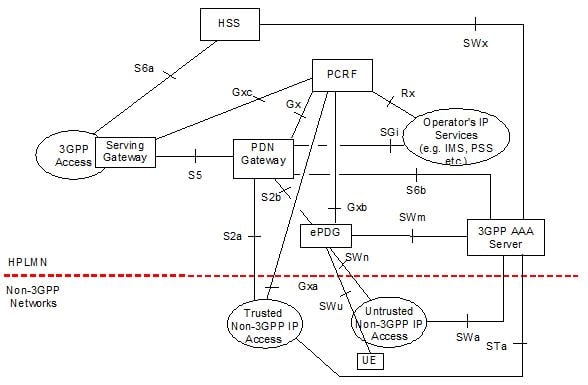
Outining a profile for supporting voice, video and SMS, IR.51 extends the requirements, detailed within IR.92 (Voice over LTE / VoLTE) and IR.94 (Video over LTE / ViLTE) to include untrusted Wi-Fi access. The PRD also stipulates the use of (dual-radio) circuit switch (CS) call continuity and fallback (VCC), per 3GPP TS 23.237. IR.51 also specifies the basic Wi-Fi radio, IMS and EPC capabilities along with describing functionality that is applicable across the protocol stack and subsystems. The VoWiFi PRD also identifies the necessary information a mobile device requires to connect to, and obtain services from, an IMS core. Furthermore, the specification outlines the subset of required telephony supplementary services and the supported media types.
Source - Internet
#GalaxyTechfluencer
- Tags:
- GalaxyTechfluencer
