Jai1
Active Level 6
Options
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
11-02-2018 01:10 PM (Last edited 03-14-2019 09:08 PM ) in
Galaxy Gallery
The most common electronic equipment used now-a-days is Cell Phone or Mobile Phone. With advancement in communication technology, the requirement of cell phones has increased dramatically. A cell phone typically transmits and receives signals in the frequency range of 0.9 to 3GHz. This article provides a simple circuit to detect the presence of an activated cell phone by detecting these signals.
I have designed two circuits that act as Cell Phone Detector Circuit, one using a combination of Schottky Diode and a Voltage Comparator and the other using a BiCMOS Op-Amp.


Circuit 1: Simple Cell Phone Detector Circuit The first circuit of the cell phone detector is a simple implementation using an Op-amp and a few other passive components. Cell Phone Detector Circuit Diagram
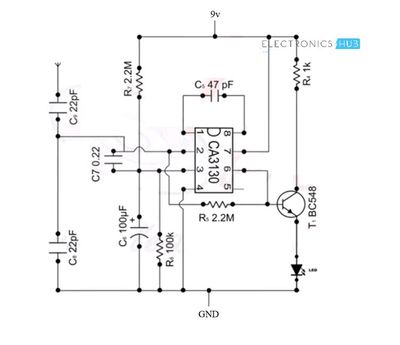
Components Required CA3130 Op-Amp Resistors – 2.2MΩ x 2, 100KΩ, 1KΩ Capacitors – 22pF x 2, 0.22nF, 47pF, 100µF BC548 NPN Transistor LED Antenna Connecting Wires Breadboard 9V Battery Working The Op-amp part of the circuit acts as the RF Signal Detector while Transistor part of the circuit act as the indicator. The capacitors collection along with the antenna are used to detect RF Signals when a cell phone makes (or receives) a phone call or sends (or receives) a text message. Op-Amp reads the signals by converting the rise in current at input to voltage at output and the LED will be activated
Mobile Phone Tracking Circuit Operation
In normal condition, when there is no RF signal, the voltage across the diode will be negligible. Even though this voltage is amplified by the transistor amplifier, yet the output voltage is less than the reference voltage, which is applied to the inverting terminal of the comparator. Since the voltage at non inverting terminal of the OPAMP is less than the voltage at the inverting terminal, the output of the OPAMP is low logic signal. Now when a mobile phone is present near the signal, a voltage is induced in the choke and the signal is demodulated by the diode. This input voltage is amplified by the common emitter transistor. The output voltage is such that it is more than the reference output voltage. The output of the OPAMP is thus a logic high signal and the LED starts glowing, to indicate the presence of a mobile phone. The circuit has to be placed centimeters away from the object to be detected.
Limitations of Mobile Phone Detector Circuit
It is a low range detector, of the order of centimetres.
VThe Schottky diode with higher barrier height is less sensitive to small signals.


Circuit 1: Simple Cell Phone Detector Circuit The first circuit of the cell phone detector is a simple implementation using an Op-amp and a few other passive components. Cell Phone Detector Circuit Diagram

Components Required CA3130 Op-Amp Resistors – 2.2MΩ x 2, 100KΩ, 1KΩ Capacitors – 22pF x 2, 0.22nF, 47pF, 100µF BC548 NPN Transistor LED Antenna Connecting Wires Breadboard 9V Battery Working The Op-amp part of the circuit acts as the RF Signal Detector while Transistor part of the circuit act as the indicator. The capacitors collection along with the antenna are used to detect RF Signals when a cell phone makes (or receives) a phone call or sends (or receives) a text message. Op-Amp reads the signals by converting the rise in current at input to voltage at output and the LED will be activated
Mobile Phone Tracking Circuit Operation
In normal condition, when there is no RF signal, the voltage across the diode will be negligible. Even though this voltage is amplified by the transistor amplifier, yet the output voltage is less than the reference voltage, which is applied to the inverting terminal of the comparator. Since the voltage at non inverting terminal of the OPAMP is less than the voltage at the inverting terminal, the output of the OPAMP is low logic signal. Now when a mobile phone is present near the signal, a voltage is induced in the choke and the signal is demodulated by the diode. This input voltage is amplified by the common emitter transistor. The output voltage is such that it is more than the reference output voltage. The output of the OPAMP is thus a logic high signal and the LED starts glowing, to indicate the presence of a mobile phone. The circuit has to be placed centimeters away from the object to be detected.
Limitations of Mobile Phone Detector Circuit
It is a low range detector, of the order of centimetres.
VThe Schottky diode with higher barrier height is less sensitive to small signals.
3 Comments
Raviijangra
★★
Options
- Mark as New
- Subscribe
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
11-02-2018 06:06 PM in
Galaxy Gallery
✌✌👍👍
PrashantShakun
Active Level 4
Options
- Mark as New
- Subscribe
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
11-03-2018 07:07 AM in
Galaxy Gallery
keep up the good work....👍👍👍
Jai1
Active Level 6
Options
- Mark as New
- Subscribe
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
11-03-2018 08:30 AM in
Galaxy Gallery
thanks prashant
