- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
07-28-2020 06:46 PM (Last edited 07-28-2020 10:03 PM ) in
Tech TalkFor detailed understanding, use a search engine. These are basics only.
Android Partitions
Boot Partition – the partition that stores the device kernel, ramdisk, firmware (modem), EFS (this contains your device IMEI, WiFi Mac address, Bluetooth Mac address, Network information, etc.).
Recovery – the partition that allows you to flash custom ROMs, kernels, etc.
System – the partition where the OS (ROM) and system apps are installed.
Data – the partition where all user apps are installed and their data stored.
Cache – the partition that holds temporary app data.
Internal Storage – the partition that saves user files like documents, pictures, videos, music, downloads, etc.
The free space that you see in any device just out of the box is your internal storage. The difference (stated capacity minus free space) is occupied by the other partitions listed above.
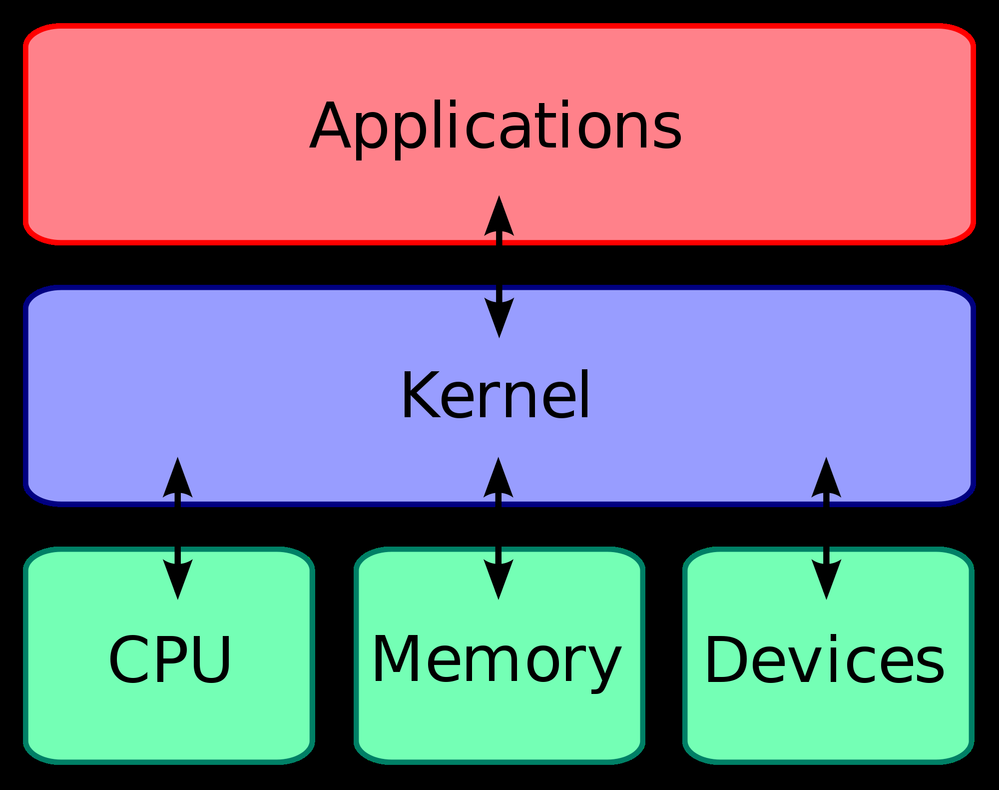
What is a kernel?
A kernel is an intermediary that tells the device/ OS what to do for a specific user action.
For example:
if you press the volume up key, the kernel tells the OS to increase the volume.
If you press the power button, the kernel decides what to do for each key combination:
boot to system if you press the power button only
boot to recovery if you press and hold power + volume down button
boot to Download mode if you press power + volume up button
Similarly, every touch-based action that we do on the screen gets an appropriate response from the OS/ device because the kernel tells the OS/ device what to do.
In simple terms, you are directly interacting with the kernel, and the kernel in turn conveys user action to the OS/ device. The kernel controls the hardware. The user as well as all applications communicate directly with the Kernel, which in turn passes on the instructions to the OS/ hardware.
You –> Kernel –> System or Recovery or Download mode
What is bootloader?
The boot partition where the Kernel, Modem, etc. resides.
Why is bootloader locked?
Boot loader is locked to protect your data. If someone tries to bypass inbuilt security and tries installing something before booting to the system, the very 1st step is to unlock the bootloader. And when bootloader is unlocked, all data is wiped, and this secures your data from being accessed by someone without authorization.
Unlocking the bootloader opens the door to other partitions like recovery, which in turn is what we need to flash ROMs, Frameworks, Mods, etc.
Once you unlock the bootloader, keep it unlocked. It is easier to fix problems on a device with an unlocked bootloader. Lock the bootloader ONLY if you want to go back to 100% stock (stock ROM, stock Kernel, stock Recovery, stock EVERYTHING!), and locking should be the very last step to return to stock.
Except for warranty claim, or reselling the device, there are hardly any benefits of re-locking the bootloader.
Samsung has E-Fuse (Knox Feature), If boot loader is unlocked or device is rooted it will be triggered.(Temporary solutions like using special code to make it look like it is not triggered are available along with few By-passing methods)
Why install a custom recovery?
1. To take a Nandroid backup. In other words, a complete system image.
2. To install non-stock software like Custom ROMs, X-posed Framework, etc. With custom ROMs, you can have access to latest Android versions not supported by phone manufacturer
3. To root your device (unlocking the bootloader or installing a custom recovery or a custom ROM does NOT root your device. It only prepares your system to be rooted)
What is root?
Rooting is gaining administrative access to your device. This involves breaking the security “wall” that is built into the OS for your own security.
Steps to root:
1. Unlock the bootloader
2. Install a custom recovery (to install custom ROMs, mods, etc.)
3. Root (your device is NOT rooted at steps 1 or 2)
Advantages and Disadvantages of Rooting
ADVANTAGES
1. AdAway - block ads by modifying hosts file and not routing traffic via a VPN
2. Firewall - control app access to internet without creating a VPN connection
3. Use dedicated VPN service while keeping ads away and firewall working
4. Titanium Backup
• freeze apps from running in the background
• disable system apps & bloatware
• prevent an app from being updated (example, YouTube AdAway)
5. Viper - amazing sound (be careful, can damage hardware)
6. Schedule automatic restart of device
7. YouTube AdAway - block YouTube ads( Vanced advantages too)
8. Greenify can hibernate apps automatically.
9. Others root apps/ mods.
DISADVANTAGES
1. Potential Security vulnerabilities
2. Some apps (like banking apps) may not work
3. Loss of manufacturer warranty
4. Potential to "brick" the device
What is Bricking?
Do remember that Kernels, ROMs, Custom Recoveries, etc. are all device specific. They are specific down to the component level. For example, devices like Samsung flagships that ship with Qualcomm processor in the USA and Exynos processor in other markets will require different custom ROMs, Recoveries, etc. Using the right files for flashing is extremely important to avoid bricking your device.
What is Bricking?
Bricking is when your device fails to boot (and is as good as a brick). There are 3 types of bricking:
Soft brick - device starts but is stuck at boot animation. This is caused by flashing an incompatible file. Easy to fix.
Hard brick - device doesn't respond at all. It can be fixed using "unbrick" tools and methods.
Permanent brick - congratulations, your device is now a brick. You can't fix it.
The post only explains the terminology and concepts.
Modifying your device is a risky affair. Do them at your own risk.
- Mark as New
- Subscribe
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
07-29-2020 07:22 PM in
Tech Talk- Mark as New
- Subscribe
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
07-29-2020 10:20 PM (Last edited 07-29-2020 10:40 PM ) in
Tech Talk- Mark as New
- Subscribe
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
07-29-2020 10:35 PM in
Tech Talk- Mark as New
- Subscribe
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
10-09-2020 12:40 AM in
Tech TalkCongratulations 🎊 Your Device is now a Brick. Now go make a building using it 🤣
- Mark as New
- Subscribe
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
04-05-2022 09:28 PM in
Tech Talk